FabricPath is a technology which combines the benefits of Routing protocols, here will be Intermediate-System-to-Intermediate-System (IS-IS), and Layer 2 Network Ethernet environments.
To list some of FabricPath advantages:
- MAC Address scalability by Conversational Learning
- No spanning-tree anymore, hurray! Each switch will have its own view of Layer 2 topology and calculates the L2 topology using SPF calculation.
- Equal cost multipath forwarding for Unicast Layer 2 traffic!
- Makes any kind of topology possible!
- Configuration/Administration is not a hassle anymore
- Loop prevention/mitigation by having a TTL field in the frames
Switch-ID
We can refer to FabricPath as “Routing MAC Addresses” or “Layer 2 over Layer 3”, but it doesn’t mean that FabricPath ports have an IP Address! In a FabricPath topology, each device is dynamically assigned a “switch-id” via Dynamic Resource Allocation Protocol (DRAP), and L2 forwarding table is populated based on reachability to each switch-id.
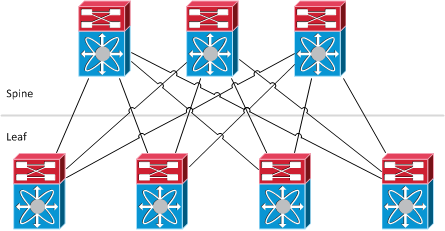
Function types in FabricPath
- Leaf: This is where Classic Ethernet devices are connected to. It’s the point of “MAC to switch-id” mapping. Traffic is looked up in the L2 forwarding table and then encapsulated into a MAC-in-MAC frame whose destination switch-id is the switch which the destination host is connected to. FabricPath is only supported on Cisco Nexus 5500 with NX-OS 5.1(3)N1(1) and higher as the edge (access) device in FabricPath topology.
- Spine: Cisco Nexus 7000 is supported as the aggregation device in FabricPath topology with NX-OS 5.1(1) and higher, but only based on F1 line cards. Layer 3 forwarding could be gained by adding M1 series cards.