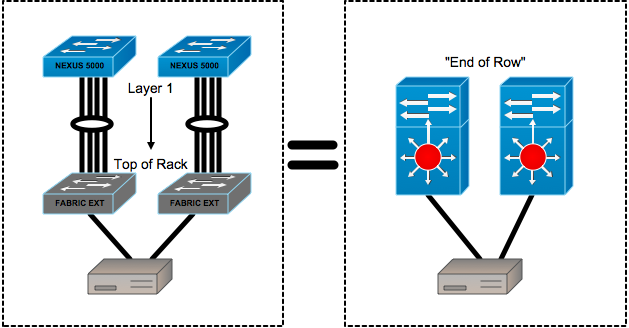
This post is my snippet of Brad Hedlund article about ToR and EoR design which is accessible via the following link:
http://bradhedlund.com/2009/04/05/top-of-rack-vs-end-of-row-data-center-designs/
Top of Rack Design
ToR is sometimes called In-Rack design.
Benefits:
- All copper cabling for servers stays within the rack as relatively
- there is no need to for a large copper cabling infrastructure
- Any network upgrades or issues with the rack switches will generally only affect the servers within that rack
- any future support of 40 or 100 Gigabit on twisted pair will likely have very short distance limitations (in-rack distances). This too is another key factor why Top of Rack would be selected over End of Row.